
Around 20:50 Beijing time on June 6, 2024, SpaceX's Starship conducted its fourth orbital flight test, still launched from the Boca Chica Starship Base on the Gulf of Mexico coast in Texas, USA.
Shortly after the launch, the booster rocket successfully landed on the sea surface as planned. The Starship flew for about an hour, and during re-entry into the atmosphere, the heat shield tiles fell off and the wing surface was burned through, but it still persisted until it landed on the sea surface, completing all the scheduled tasks and goals.
Tonight's test flight is the first time in the history of SpaceX's super rocket "Starship" that all tasks have been completed. SpaceX founder Elon Musk announced that the "Starship" successfully made a soft landing on the ocean, congratulating the SpaceX team on the great achievement.
In Musk's vision, "Starship" is the carrier that will send humans to Mars, which is also the core goal of his founding of SpaceX. Thanks to the rapid development momentum, the valuation of SpaceX is soaring. At the end of May this year, media reports cited informed sources as saying that Musk's SpaceX has begun discussions to sell existing shares, and the company's valuation may reach $200 billion (about 1.45 trillion yuan).
The Starship completes its fourth test flight: successfully splashes down in the Indian Ocean.
According to the schedule provided by SpaceX, after the Starship ignites and takes off at 20:50 Beijing time, the entire test flight process will last about 66 minutes.
20:50 Beijing time: The Starship combination ignites and takes off.

20:51 Beijing time: The rocket reaches the maximum aerodynamic pressure.
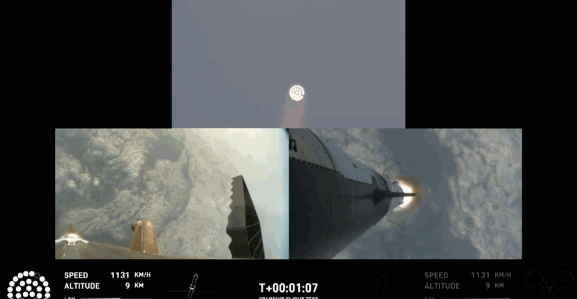
20:52 Beijing time: The Starship spacecraft successfully implements thermal separation from the "Super Heavy" rocket, and at the same time, the "Super Heavy" rocket performs a flip maneuver and a retrograde ignition.
20:54 Beijing time: The thermal separation ring ejection.

20:57 Beijing time: The "Super Heavy" rocket successfully splashes down in the Gulf of Mexico, and SpaceX employees cheer and celebrate.
20:58 Beijing time: The Starship spacecraft engine is successfully shut down.
Around 21:00 Beijing time: The Starship spacecraft is flying in Earth's orbit, and there is no video signal during this stage, but the instruments show that the spacecraft is in normal condition.

Around 21:28 Beijing time: The signal is restored, and the Starship spacecraft is flying steadily. It will re-enter the atmosphere in about 10 minutes, which will be the most critical step of this test flight.
21:48 Beijing time: The spacecraft has reached the thickest part of the atmosphere, and it seems that the spacecraft is starting to struggle.
21:55 Beijing time: The spacecraft successfully implements the landing ignition and flip, and successfully splashes down in the Indian Ocean. SpaceX employees are ecstatically celebrating!

Subsequently, SpaceX announced that the Starship itself confirmed splashing down in the Indian Ocean, and the fourth test flight was a success.
Musk also announced the latest news in the first place: "Despite losing many tiles and the flap being damaged, the Starship still successfully made a soft landing on the ocean! Congratulations to the @SpaceX team for the great achievement!"
Last Saturday, Musk wrote on social media: "The main goal of this mission is to fly further during re-entry into the atmosphere, preferably to withstand the highest temperature."
According to the SpaceX website, the new generation heavy-lift launch vehicle "Starship" is the largest and most powerful rocket in the world to date, with a total height of about 120 meters and a diameter of about 9 meters. The rocket consists of two parts: the bottom is the "Super Heavy" booster, which is about 69 meters high and equipped with multiple "Raptor" engines; the top is the spacecraft, about 50 meters high, and is reusable. Currently, NASA's investment in the project is close to 4 billion US dollars.
The nearly 400-foot (approximately 121-meter) tall rocket is built to transport astronauts to the moon for NASA, and its ultimate goal may be to one day send humans to Mars.
According to reports, in 2023, the United States launched a total of 116 rockets, with SpaceX accounting for 98 of them. The former quasi-national team - ULA (United Launch Alliance, jointly established by Boeing and Lockheed Martin) only launched three times.
According to Musk's plan, in 2024, when only the Falcon (including the Falcon Heavy) is available, SpaceX will launch 144 times, accounting for 90% of the global total mass in orbit, which is 10 times the sum of the others.
Once the Starship is mature, SpaceX's mass in orbit will account for 99% of the global total, which is 100 times the sum of the others.
In terms of revenue, estimates show that in the past three years, SpaceX's revenue has achieved consecutive doubling growth, from 2.3 bln in 2021 to 8.7 billion, and in 2023, it even achieved quarterly profitability for the first time, becoming an important milestone for this business model.


 川公网安备 51019002001991号
川公网安备 51019002001991号





